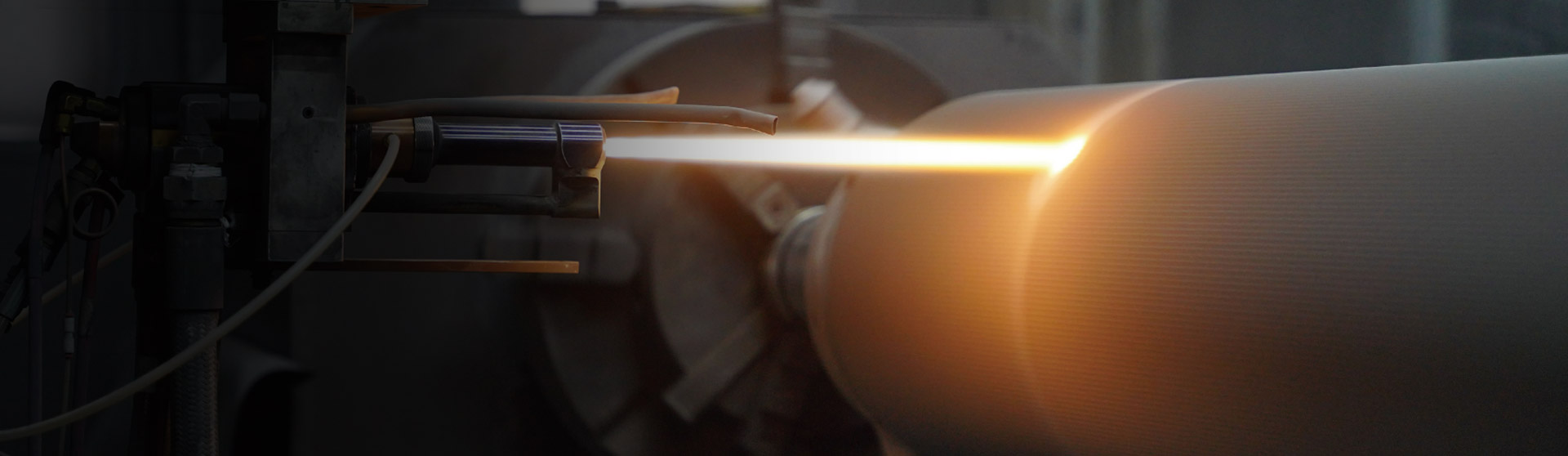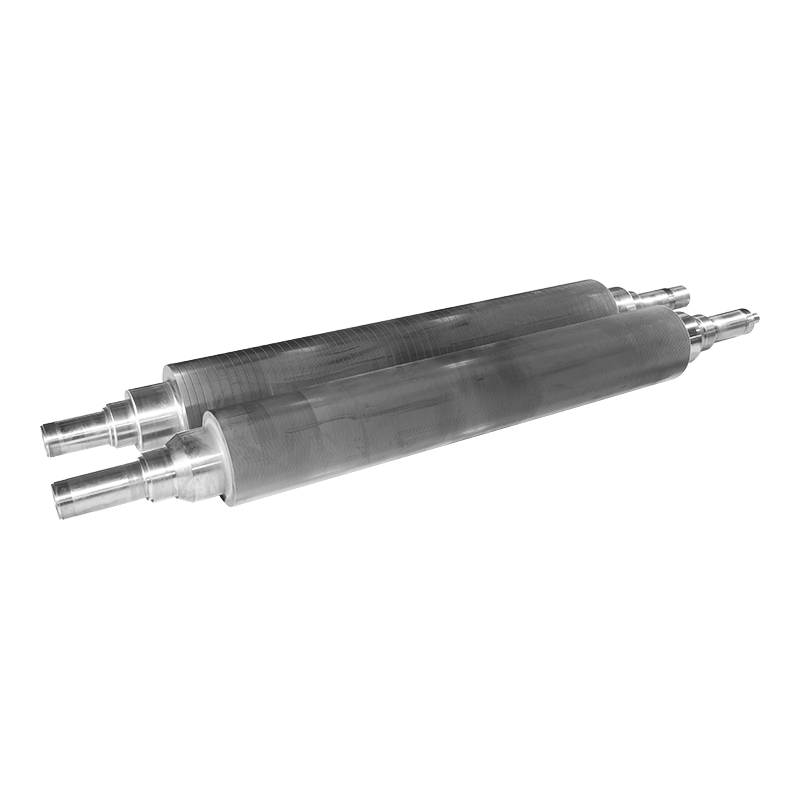
Corrugating rollers are essential components in the production of corrugated cardboard. They shape and emboss paper sheets, creating the fluted layers that give cardboard its strength and durability. The performance, longevity, and efficiency of these rollers largely depend on the materials used in their construction.
Steel Rollers
Steel is one of the common materials used for corrugating rollers. High-quality carbon steel or alloy steel provides strength and resistance to wear. Steel rollers are often heat-treated to enhance hardness and durability, which is critical for handling continuous high-speed production.
A roller made from steel can maintain precision and dimensional stability even under heavy loads and high temperatures. Many corrugating equipment manufacturers choose steel rollers for their reliability and consistent performance over long periods of use.
Chrome-Plated Rollers
Some corrugating rollers feature chrome plating on a steel base. The chrome layer increases surface hardness and provides resistance to corrosion, abrasion, and chemical exposure. Chrome-plated rollers also offer a smoother surface, which reduces friction and prevents sticking of paper fibers during production.
By using chrome-plated rollers, operators can extend service life and maintain consistent corrugation quality. This combination of steel strength and chrome durability makes them suitable for high-speed and high-volume corrugating lines.
Rubber-Covered Rollers
Rubber coverings are another material choice for corrugating rollers, particularly in medium-speed or specialty applications. Rubber provides flexibility, allowing for better control over pressure distribution and reducing the risk of paper tearing.
Different types of rubber, such as natural rubber or synthetic compounds, are selected based on their hardness, elasticity, and resistance to wear. A rubber-covered corrugating roller can help achieve uniform fluting while absorbing some of the impact and vibration during operation.
Polyurethane Rollers
Polyurethane is increasingly used as a roller covering due to its durability and versatility. It combines the resilience of rubber with higher resistance to abrasion and chemical wear. Polyurethane-covered rollers can operate effectively in environments where standard rubber might degrade more quickly.
A corrugating roller with a polyurethane layer can also maintain consistent pressure over time, ensuring uniform corrugation quality. Many manufacturers choose polyurethane coverings for medium- to high-volume production lines where consistent performance is essential.
Composite Materials
Some modern corrugating rollers use composite materials, combining metal cores with polymer or rubber coatings. This design balances the strength of the metal with the flexibility or abrasion resistance of the outer layer.
Composite corrugating rollers are lighter than all-metal rollers, which can reduce energy consumption and minimize wear on bearings and other machine components. These rollers are often found in specialized or high-efficiency corrugating machines.
The materials used in corrugating rollers—steel, chrome-plated steel, rubber, polyurethane, and composites—play a significant role in the performance and durability of corrugating machines. Steel provides strength, chrome adds surface hardness, rubber and polyurethane offer flexibility and wear resistance, and composites balance these properties for specialized applications.
Choosing the right material depends on production speed, paper type, and operational requirements. By selecting the appropriate corrugating roller material, manufacturers can ensure consistent quality, reduce maintenance, and improve overall efficiency in their corrugated board production lines.

 English
English  Español
Español  Português
Português  عربى
عربى